jQuery 1.4.2 Released
jQuery 1.4.2 is now out! This is the second minor release on top of jQuery 1.4, fixing some outstanding bugs from the 1.4 release and landing some nice improvements.
I would like to thank the following people that provided patches for this release: Ben Alman, Justin Meyer, Neeraj Singh, and Noah Sloan.
Downloading
As usual, we provide two copies of jQuery, one minified (we now use the Google Closure Compiler as the default minifier) and one uncompressed (for debugging or reading).
- jQuery Minified (24kb Gzipped)
- jQuery Regular (155kb)
You can feel free to include the above URLs directly into your site and you will get the full performance benefits of a quickly-loading jQuery.
Additionally you can also load the URLs directly from either Google or Microsoft’s CDNs:
- http://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.4.2/jquery.min.js
- http://ajax.microsoft.com/ajax/jQuery/jquery-1.4.2.min.js
New Features
A full list of the API changes can be found in the 1.4.2 category on the jQuery API site.
In this release we’ve added two new methods: .delegate() and .undelegate(). These methods serve as complements to the existing .live() and .die() methods in jQuery. They simplify the process of watching for specific events from a certain root within the document.
For example:
$("table").delegate("td", "hover", function(){
$(this).toggleClass("hover");
});
This is equivalent to the following code written using .live():
$("table").each(function(){
$("td", this).live("hover", function(){
$(this).toggleClass("hover");
});
});
Additionally, .live() is roughly equivalent to the following .delegate() code.
$(document).delegate("td", "hover", function(){
$(this).toggleClass("hover");
});
What’s Changed?
There has been some large code rewrites within this release, both for performance and for fixing long-standing issues.
Performance Improvements
As is the case with virtually every release of jQuery: We’ve worked hard to continue to improve the performance of the code base, making sure that you’re provided with the best performing JavaScript code possible.
According to the numbers presented by the Taskspeed benchmark we’ve improved the performance of jQuery about 2x compared to jQuery 1.4.1 and about 3x compared to jQuery 1.3.2.
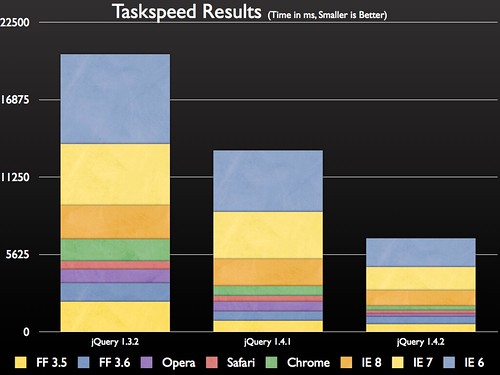
Specifically we’ve improved the performance of 4 areas within jQuery:
- The performance of calling .bind() and .unbind(). (Ticket)
- The performance of .empty(), .remove(), and .html(). (Ticket)
- The performance of inserting a single DOM node into a document. (Ticket, Additional Commit)
- The performace of calling
$("body"). (Commit)
While comprehensive benchmarks like Taskspeed can be interesting if deconstructed into individual sub-tests for further study, as a project we tend to stay away from using them as an accurate measure of true, overall, library performance. Considering how many aspects make up a library, not to mention the different techniques that they offer, cumulative results rarely reflect how an actual user may use a library.
For example, we saw significant overall performance speed-ups in Taskspeed simply by optimizing the $("body") selector because it’s called hundreds of times within the tests. Additionally we saw large gains by optimizing .bind() and .unbind() by a fraction of a millisecond – an inconsequential amount – especially considering that any cases where you would bind hundreds of events you would likely want to use .live() or .delegate() instead.
We’ve collected some results from the other major libraries as well but are less interested in those results and far more interested in the performance improvements that we’ve made relative to older versions of jQuery itself.
We will continue to work on optimizing the jQuery code base – indefinitely. It’s always a major concern for us to try and provide the fastest JavaScript/DOM-development experience possible. And yes, there will likely always be ways to gain additional performance – either through internal optimizations or by pushing critical functionality off into browser-land for standardization.
Event Rewrite
The largest internal changes have come through a much-needed structural rewrite of the events module. Many quirky issues related to event binding have been resolved with these fixes.
Namely event handlers are no longer stored as object properties in jQuery’s internal object store (with metadata attached to the handlers). Instead they’re now stored within an internal array of objects.
If you’ve ever had the opportunity to play around with .data("events") on a jQuery element you would find that it returns an object with all the event types currently bound, within it.
To enumerate some of the changes that have occurred during this rewrite:
- It’s now possible to bind identical handlers with different data, namespaces, and event types universally.
- Execution of event handlers will continue after one handler removes itself (or its sibling handlers).
- We no longer attach data/namespace information directly to the event handlers (only a unique tracking ID).
- We no longer use proxy functions, internally, to try and encapsulate handlers.
- Execution order of events is now guaranteed in all browsers. Google Chrome had a long-standing error in their object-looping logic that has been routed around.
As a side-effect of these changes we had to change the newly-exposed special add/special remove APIs in order to accommodate the new event data objects. Ben Alman is in the process of writing up a large tutorial on jQuery’s special event system and we will be making additional announcements when that occurs.
Bug Fixes
There were a total of 40 tickets closed in this minor release. Some relating to differences between jQuery 1.3.2 and jQuery 1.4.x, some fixing long-standing issues (like in the case of the event module rewrite).
Raw Data
This is the raw data that we collected to generate the aforementioned charts.
jQuery 1.3.2 jQuery 1.4.1 jQuery 1.4.2 Prototype 1.6.1 MooTools 1.2.4 Dojo 1.4.1 YUI 3.0.0 FF 3.5 2182 806 565 2156 1073 575 1885 FF 3.6 1352 677 519 2067 857 750 1494 Opera 983 697 222 793 678 218 1201 Safari 610 435 252 315 235 238 612 Chrome 1591 703 293 271 312 222 745 IE 8 2470 1937 1141 3045 4749 1420 2922 IE 7 4468 3470 1705 9863 10034 1737 5830 IE 6 6517 4468 2110 13499 11453 2202 7295